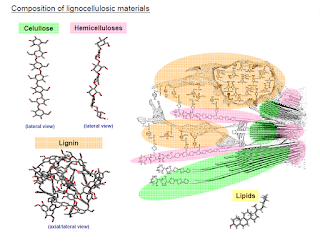
Flax or linen is a multicellular, vegetable bast fiber like jute and hemp. Cellulose is the most part of its composition.
Physical properties of Linen/Flax
Length: Flax fibers range up to 90 cm.
Diameter: This fiber has an average 12 to 16 micron diameter.
Strength: More than cotton fiber, 5.5 to 6.5 gm/denier.
Elastic Property: Elasticity is too much low. Extension before breaking 2.7 to 3.5%.
Moisture Regain: MR% of linen fiber is 10 to 12%
Abrasion Resistance: Moderate
Color: Yellowish to gray.
Luster: More than cotton fiber, slightly silky.
Heat Resistance: Better than cotton fiber.
Chemical Properties: Like cotton linen/flax fiber is a cellulose polymer, but the structure of it is more crystalline which makes it stronger, crisper and hard to handle and more easily wrinkled. They absorb and release water quickly, making linen comfortable to wear in hot weather. The resistance against concentrated acid is poor but dilute acid can not affect more. It works well though use strong alkali and the cold bleaching agent. It is not affected by mildew and insects as well. Dyeing properties of linen is not so good as cotton or jute, Direct or Vat colors are suitable to dye up this fiber.
Application
The most usual applications of linen/flax fiber
It burns without any smell thus it is used for cigarette covering.
Physical properties of Linen/Flax
Length: Flax fibers range up to 90 cm.
Diameter: This fiber has an average 12 to 16 micron diameter.
Strength: More than cotton fiber, 5.5 to 6.5 gm/denier.
Elastic Property: Elasticity is too much low. Extension before breaking 2.7 to 3.5%.
Moisture Regain: MR% of linen fiber is 10 to 12%
Abrasion Resistance: Moderate
Color: Yellowish to gray.
Luster: More than cotton fiber, slightly silky.
Heat Resistance: Better than cotton fiber.
Chemical Properties: Like cotton linen/flax fiber is a cellulose polymer, but the structure of it is more crystalline which makes it stronger, crisper and hard to handle and more easily wrinkled. They absorb and release water quickly, making linen comfortable to wear in hot weather. The resistance against concentrated acid is poor but dilute acid can not affect more. It works well though use strong alkali and the cold bleaching agent. It is not affected by mildew and insects as well. Dyeing properties of linen is not so good as cotton or jute, Direct or Vat colors are suitable to dye up this fiber.
Application
The most usual applications of linen/flax fiber
- Table wear
- Suiting
- Clothing apparel
- Surgical thread
- Sewing thread
- Decorative fabrics
- Bed linen
- Kitchen towels
- High quality papers
- Handkerchiefs
- Draperies
- Upholstery
- Wall coverings
- Artists canvases
- Luggage fabrics
- Panelling
- Insulation, filtration
- Light aviation use (fabrics)
- Reinforced plastics and composites

It burns without any smell thus it is used for cigarette covering.
Flax/Linen fiber properties and application
Advertisements
Flax or linen is a multicellular, vegetable bast fiber like jute and hemp. Cellulose is the most part of its composition.
Physical properties of Linen/Flax
Length: Flax fibers range up to 90 cm.
Diameter: This fiber has an average 12 to 16 micron diameter.
Strength: More than cotton fiber, 5.5 to 6.5 gm/denier.
Elastic Property: Elasticity is too much low. Extension before breaking 2.7 to 3.5%.
Moisture Regain: MR% of linen fiber is 10 to 12%
Abrasion Resistance: Moderate
Color: Yellowish to gray.
Luster: More than cotton fiber, slightly silky.
Heat Resistance: Better than cotton fiber.
Chemical Properties: Like cotton linen/flax fiber is a cellulose polymer, but the structure of it is more crystalline which makes it stronger, crisper and hard to handle and more easily wrinkled. They absorb and release water quickly, making linen comfortable to wear in hot weather. The resistance against concentrated acid is poor but dilute acid can not affect more. It works well though use strong alkali and the cold bleaching agent. It is not affected by mildew and insects as well. Dyeing properties of linen is not so good as cotton or jute, Direct or Vat colors are suitable to dye up this fiber.
Application
The most usual applications of linen/flax fiber
It burns without any smell thus it is used for cigarette covering.
Physical properties of Linen/Flax
Length: Flax fibers range up to 90 cm.
Diameter: This fiber has an average 12 to 16 micron diameter.
Strength: More than cotton fiber, 5.5 to 6.5 gm/denier.
Elastic Property: Elasticity is too much low. Extension before breaking 2.7 to 3.5%.
Moisture Regain: MR% of linen fiber is 10 to 12%
Abrasion Resistance: Moderate
Color: Yellowish to gray.
Luster: More than cotton fiber, slightly silky.
Heat Resistance: Better than cotton fiber.
Chemical Properties: Like cotton linen/flax fiber is a cellulose polymer, but the structure of it is more crystalline which makes it stronger, crisper and hard to handle and more easily wrinkled. They absorb and release water quickly, making linen comfortable to wear in hot weather. The resistance against concentrated acid is poor but dilute acid can not affect more. It works well though use strong alkali and the cold bleaching agent. It is not affected by mildew and insects as well. Dyeing properties of linen is not so good as cotton or jute, Direct or Vat colors are suitable to dye up this fiber.
Application
The most usual applications of linen/flax fiber
- Table wear
- Suiting
- Clothing apparel
- Surgical thread
- Sewing thread
- Decorative fabrics
- Bed linen
- Kitchen towels
- High quality papers
- Handkerchiefs
- Draperies
- Upholstery
- Wall coverings
- Artists canvases
- Luggage fabrics
- Panelling
- Insulation, filtration
- Light aviation use (fabrics)
- Reinforced plastics and composites

It burns without any smell thus it is used for cigarette covering.
Advertisements